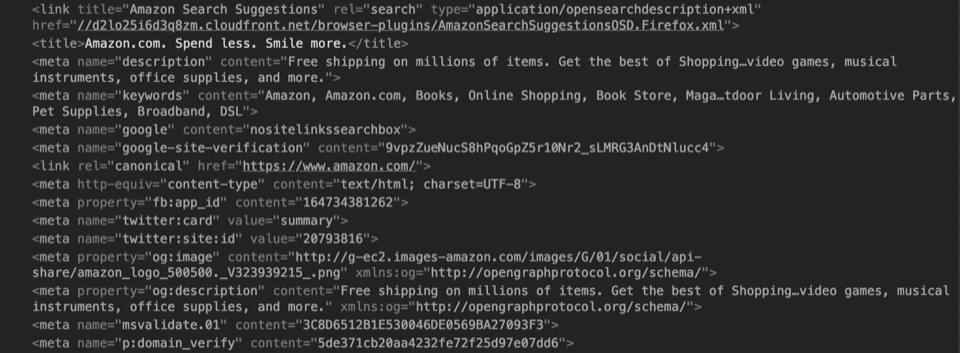
Dealing with the technicalities of SEO can be overwhelming. Yet when managing a business website or blog, it’s essential to learn about the SEO factors that boost your rankings in search engines.
Meta tags tell search engines crucial information about your web pages so they know how to display your site in the search results. When done correctly, meta tags increase your site’s visibility for relevant search terms. If done poorly, they can negatively affect your website’s ranking.
This guide explains what meta tags are, why they matter for SEO, and the best practices for writing them.
What are Meta Tags?
Meta tags are short snippets of text or code that describe a particular page’s content. The main difference between this kind of metadata and other tags with SEO value such as headers is that meta tags only exist in the HTML source code. They aren’t visible on the website itself.
This is perhaps why so many web designers forget about meta tags. A whopping 67% of websites are missing meta descriptions, and about half of all websites have duplicate title tags and meta descriptions.
Why It’s Important for SEO
Meta tags are one of the primary channels that a website uses to communicate with search engine robots, which are responsible for crawling the content of web pages for indexing. Meta tags indicate to search engines whether a web page should be indexed or not, and they provide information about its content.
As a result, meta tags should be a core component of your SEO strategy. With the proper configuration of meta tags and good writing, those search engine bots will have a better understanding of the content on your pages so that you can rank higher.
Meta tags also provide quality information to users to increase their click-through rate (CTR), providing another reason to optimize metadata.
Different Types of Meta Tags and Best Practices for Each
Each type of meta tag plays a unique role in presenting a website to search engines. Here are the most important types of meta tags you’ll need to know and the best practices for each of them:
Meta Title
The meta title is the name of a web page as it appears on the search engine results page (SERP). page of a website. This tag is the first thing potential site visitors see, and it should serve as both a “hook” and a summary of what the page is about.
Best Practices for Title Tags
Meta titles are used for indexing and attracting visitors, so they should be click-worthy yet also accurate in describing the web page. Here are several tips for writing a great meta title:
- Pay attention to the length: Title tags should be between 50 and 60 characters. Longer than that, Google and other search engines will cut off the text.
- Avoid keyword stuffing: Choose one or two keywords to focus on and build your title around that. Google’s algorithms have gotten smarter over time. Web crawlers can recognize keyword-stuffed and spammy websites, and attempts to game the system will only hurt your ranking.
- Match search intent: Never include a title that doesn’t describe what the webpage is about since that will hurt key metrics such as bounce rate and time spent on the page.
- Place a target keyword at the beginning of the title: One study showed that people see about two words of a title tag before scanning past it, meaning placing the keyword at the start will draw more attention and increase clicks.
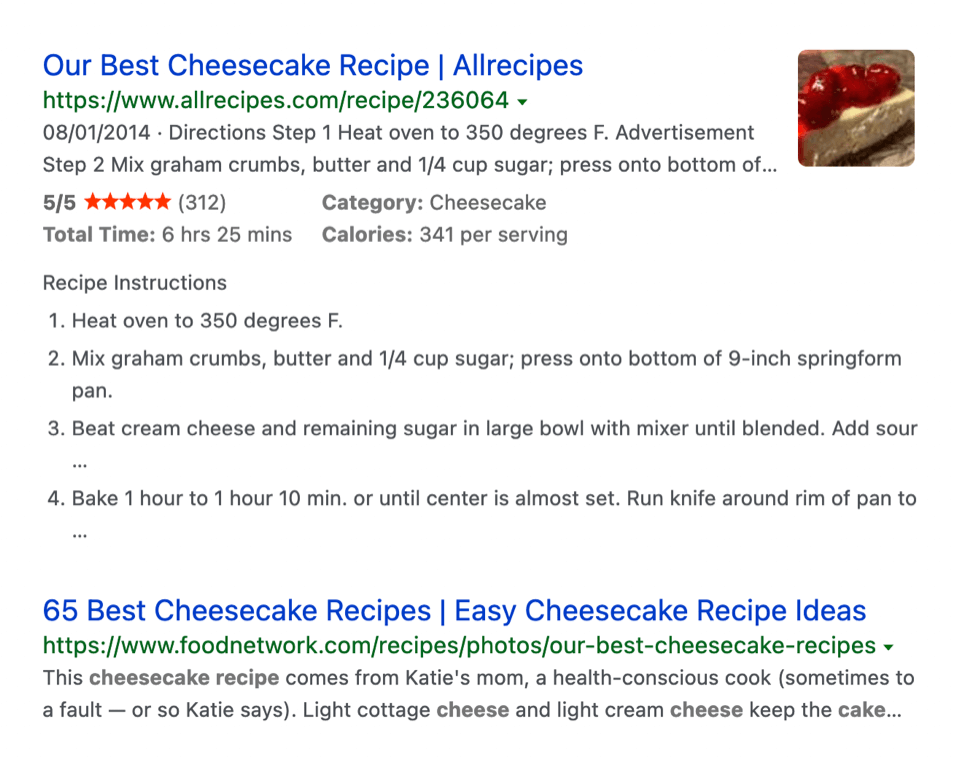
Here’s an example of a title tag from the search team “cheesecake recipe.” Observe the keyword “cheesecake recipe” and the website name, confined to the character limit.
Meta Description
SEO metadata requires a description in addition to the title tag. A meta description is a text that summarizes the information on the web page and why it matters.
Meta descriptions should inform and interest users with a short and relevant summary of what a particular page is about. They’re placed within the HTML code and also appear on the search engine results pages underneath the title tags.
While meta descriptions aren’t a direct Google ranking factor, they affect the CTR and improve search rankings. Therefore, it’s vital to write relevant and crisp meta descriptions that entice searchers to want to click on your page.
Best Practices for Meta Descriptions
Remember, the SEO value of a description meta tag comes primarily to motivate people to click on your content.
- Provide an accurate summary: Always provide specific information about what someone should expect when they click on your page. Being coy or click-baity can be a turn-off to people who don’t know your website very well.
- Focus on the benefits: Tell searchers about the value they’ll receive from clicking on your web page.
- Use the appropriate length: The optimal length for a meta description is between 150 to 160 characters. Google and other search engines cut off meta descriptions that exceed the 160-character limit.
- Include the target and secondary keywords: Include your target keyword in your unique meta description, and also include secondary keywords or search terms. When a user searches for those terms, Google will highlight them on the SERP.
- Write compelling copy: Use a strong call to action and create a desire for the reader to know more.
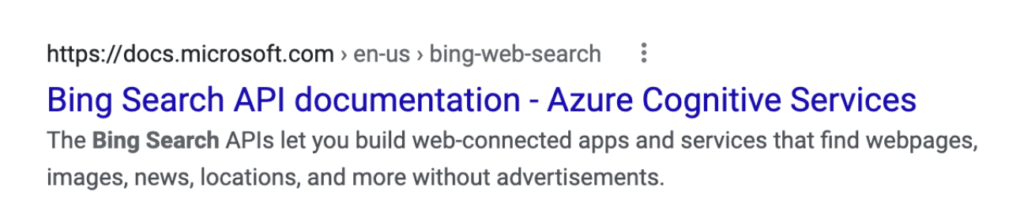
In the example below, the meta description is concise, informative, and directed at the user.
Meta Robots
Meta robots are another meta tag critical for SEO that informs search engine crawlers whether they should index a particular page or not. There are four distinct values of a robots.txt meta tag.
- Index – this tag tells the bot crawlers to index a web page.
- Noindex – this tag tells the crawlers not to index a web page.
- Follow – this tag informs the crawlers to follow all links on a page.
- Nofollow – this tag directs the crawlers not to follow the page and any links on that page.
By default, search engines follow and index all pages unless specified otherwise. For this reason, it’s most useful to add robots.txt when you don’t want a page indexed.
Best Practices for Meta Robots
While meta robots may seem complex, they don’t have to be.
- Use plugins. Plugins like Yoast SEO allow you to easily update a page’s code.
- Use robots tags to restrict Google from crawling a page. While this may seem counterintuitive to your metadata SEO strategy, removing unimportant, irrelevant, or duplicate pages from your index may help your more prominent pages rank higher.
Meta Refresh Redirect
Meta refresh redirects are client-side redirects. Unlike the typical 301 and 302 redirects that happen on the webserver, this redirect takes the web browser to a different web page after a specified time span. Meta refresh redirects are most commonly known for the five-second countdown with a text that reads, “if you aren’t redirected in five seconds, click here.”
Here’s why you should use meta refresh redirect when moving content:
Help search engines better understand your site: Redirects tell Google and other search engines where your content has moved to and whether this move is temporary or permanent. This directly affects how the pages appear in their search results.
Better user experience for visitors: It’s never good when your visitors are hit with the common “page not found” message when they’re trying to access information. Redirects resolve this issue by seamlessly sending visitors to the content’s new location.
Best Practices for Meta Refresh Redirect
This type of meta tag helps your SEO if you’ve recently moved content from one URL to another or you’ve deleted content. Here are a few common cases where you’ll want to use these redirects.
- When merging websites: If you’re merging several websites into one, you’ll want to permanently redirect old URLs into new URLs.
- When switching to HTTPS: When switching from HTTP to HTTPS, you’ll need to permanently redirect every unsecured (HTTP) page and resource to its secure (HTTPS) location.
- When moving domains: If you’re rebranding your site and moving from one domain to another, you’ll want to permanently redirect all your pages on the old domain to the pages on the new domain.
- When deleting pages: When removing content from one site, you should permanently redirect its URL to a relevant and similar page when possible. This ensures that all backlinks to the old page still count for SEO purposes and that any internal links still work.
When running a promotion: When you’re running a temporary promotion and want to send visitors from, say, domain.com/shoes to domain.com/shoes-black-Friday-deals, you’ll want to use a temporary redirect.
Meta Charset
The meta charset tag determines the character encoding for your page—another important consideration for SEO. In essence, it informs the browser how the text on your web page should be displayed. Poor encoding can cause characters to be displayed incorrectly.
That can lead to SEO troubles like:
- Other websites don’t want to link to your pages.
- Low time on page, high bounce rate, low time on page, and low dwell time.
- Crawlers and search engine bots won’t understand your content to properly index your pages.
Google recommends using Unicode/UTF-8 where possible.
Best Practices for Meta Charset
Here are a few rules you’ll want to stick to so that your characters display properly on your pages:
- Use meta charset on all pages.
- Choose the correct syntax for your specific HTML code.
- Use UTF-8 when possible.
Meta Viewport
As a final SEO meta tag, site designers need to consider meta viewpoints. Since 52.2% of website traffic worldwide comes from mobile phones, it’s important to ensure your website is properly optimized for all devices. A meta viewport meta tag assists in making your website more mobile responsive and helps to manage the layout of your pages when viewed on mobile browsers.
So, a viewport meta tag lets your web pages scale as per the dimensions of the mobile device. Not properly using the viewport meta tag will load the page in a way that is not compatible with mobile phones and will negatively impact the user experience and search rankings.
Best Practices for Meta Viewport
How do you ensure your website has a mobile responsive design? Here are some best practices for meta viewport:
- Don’t use absolute width values in your CSS: Absolute values result in the elements of your site loading wider than your viewport allows. Instead, use relative width values.
- Avoid rendering your site to a specific width. Widths typically vary from one device to another. For example, the width of a smartphone is different from that of a laptop or tablet.
- Use a meta viewport tag on all pages. This helps your website adapt the content for the mobile version.
Conclusion
Although many people ignore it, metadata is crucial for SEO. Meta tags allow bots to crawl and index your site so that search engines can properly rank your pages. Additionally, they can influence searchers’ decisions to click through to your page, thus affecting your click-through rates. Put in the time to increase your traffic by optimizing your meta tags for SEO—or, partner with an agency that can put in the time for you.
Need help finding an SEO agency? BESTSEO helps you find the right SEO and digital marketing agency so you can attract the right audience to your site and see the growth in leads and sales you’re looking for.